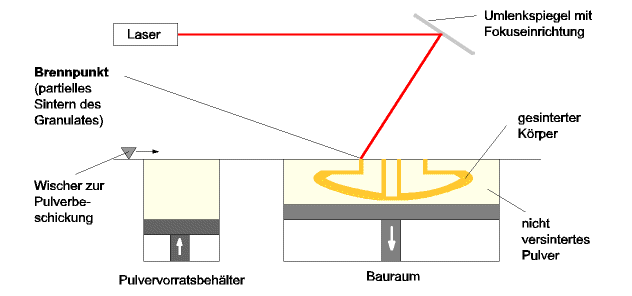
Selectives Laser Sintern (SLS)
The process of Selective Laser Sinter produces a prototype through a layered, temperature-conditional sinter, or melting, of powdered source materials like polymers, metal, ceramic, wax and also mixtures of these. The sinter results with help from a laser beam. The unbound powder material remains in the build space and becomes the support of the part so that no additional support construction is necessary.
The building process is generally followed by a simple finishing process. The part, regardless of the material, can be cleaned with pressured air and/or brush. It is also possible to sand or the polish the part. Except for parts made from ceramic, no post curing is necessary.

Picture: Illustration of the Selective Laser Sinter Process
Application:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|