Layer Laminated
Manufacturing
(LLM)
An adhesive coated material made
out of paper, plastic or metal foil is glued layer after layer on a
build platform and respectively on the previous layers of the model.
With a laser beam, the contour of one slice-layer is drawn on and
therefore cut into the foil. The neutral market name for this process
is layer laminated manufacturing (LLM). The leftover Material serves as
a support construction for the part.
After termination of the build process
the part is removed with simple hand tools and the surface is treated
with sandpaper. Finally, the surface is sealed with wax or lacquer.
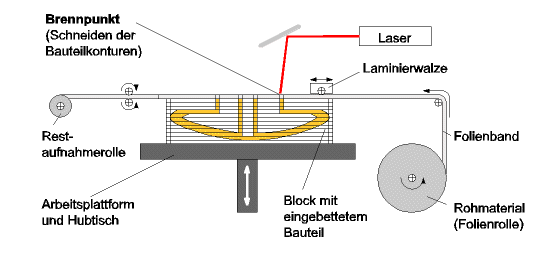
Picture: Illustration of the Layer
Laminated Manufacturing Process
Applications:
- Conception in form of:
- Models for direct use
(inspection)
- Models for casting in
silicon
- Function models for tools, as
short
term benchmark, in the form of:
- Foundry models
- Prototype parts
- Prototypes of
small series
tools
in the form of:
- Laminar forming
- Forming for fabrication Casting
part
cores
- Forming for fabrication of
hard
form
parts.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
- Fast process
(laser must
only
draw the contour)
- No post hardening
process
- Practically no inner stress
that
causes undesirable deformations (shrinking, delay)
|
- Not good for sheer walls in
z-direction
- Interchangeable use for
complex
parts
- Necessary post processing
to
protect for intruding moisture (swelling)
- Several parts in one another
impossible to make (also not reasonable)
- No application of the
leftover
material
|

