Fused Layer
Manufacturing
(FLM)
The building of a prototype using this
process begins with the melting of the materials. This material is
directed and applied on the part. The formation of the layers occurs
through solidification as a result of heat conduction. This
process demands the construction of a support structure throughout the
build process to hold the piece.
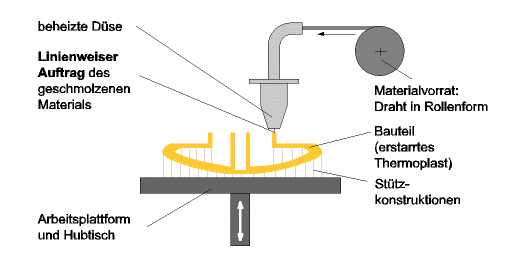
Picture: Illustration of the Fused
Layered Manufacturing Process
Applications:
- Concept models
- Part for pass- form- function
control
for later manufacturing sequences
- Lost model for Investment and
Injection molding
- For processing in following
processes
(Fein-, Vacuum, Injection processes)
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
- Low machine
dimensions
- Fast
- Cost effective
- Manufacture more
compact
work
pieces (bigger through current material filled surfaces)
- No dangerous processes
(laser
beams, chemicals)
|
- Limited
Accuracy
- Limited Material
variety
- Smaller build room hence
only
small parts are possible
- Support construction
necessary
|

